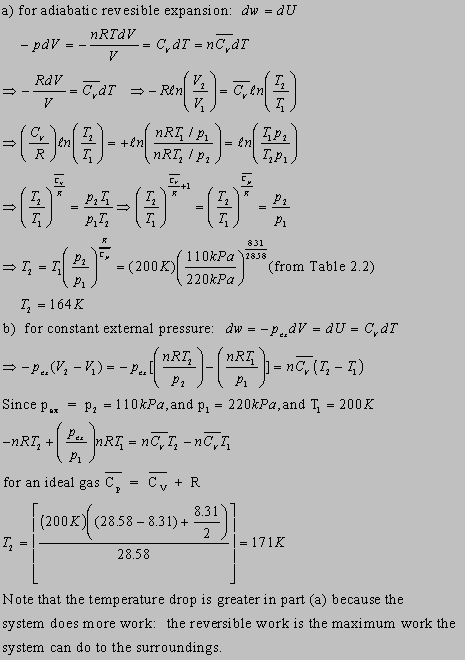
HOMEWORK #3
SEPTEMBER 14, 1998
SOLUTIONS
Chapter 2, Exercises #2.25(b), 2.26(b), 2.29(b). 2.34(b), 2.35(b),
2.36(b), 2.39(b), 2.42(b), 2.43(b); Problem 2.2. Data from Tables
2.5 and 2.6 (in text Appendix).
2.25(b)
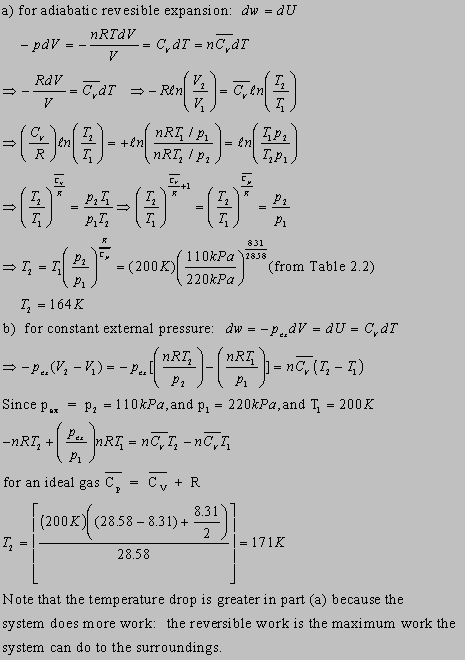
2.26(b)

2.29(b)
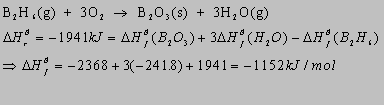
2.34(b)
AgBr(s) Ag+(aq) + Br-(aq)
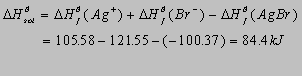
2.35(b)
C(gr) + O2(g) CO2(g) H1 = -393.51 kJ/mol
C(dia) + O2(g) CO2(g) H2 = -395.41
kJ/mol
By subtraction: C(gr) C(dia) H3 = H1 - H2
= -393.51-(-395.41) = 1.9kJ
2.36(b)
for glucose: M = 180.16g/mol; Hcomb = -2808 kJ/mol
Therefore, for 2.5g, (2.5g/180.16g/mol)(-2808kJ/mol) = 38.97kJ
w = mgh = (38.97x103J)(0.25) = (65kg)(9.81m/s2)h
h = 15.28m
2.39(b)a) C3H6(cyclopropane) C3H6(propene)
Hr = Hf(propene) - Hf(cyclopropane)
= 20.42 - 53.3 = -32.9kJ
b) HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
For strong electrolytes, the reaction is just H+ (aq) + OH-(aq)
H2O(l)
Hr = Hf(H2O)- Hf(OH-)
- Hf(H+) = -285.83 - (-229.99) - (0) = -55.84kJ
2.42(b) 2NOCl(g) 2NO(g) + Cl2(g)
Hr = 2Hf(NO) + Hf(Cl2) -
2Hf(NOCl)
Hf(NOCl) = 0.5[2(90.25) + 0 - 75.5] = 52.5kJ
2.43(b)
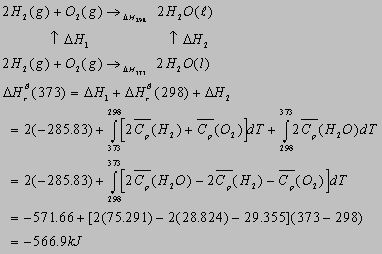
2.2 For water p = 75.291J/mol-K and Hvap
= 44.016kJ/mol at 298K
The equivalent mass of water = 65kg 65x103g/18g/mol = 3.611x103mol
For the input of 10MJ per day of heat energy,
T = q/Cp = 10x106J/(3.611x103mol)(75.291J/mol-K)
= 36.78K = 36.78C = 66.21F
Need to absorb the 10MJ by evaporation, H2O(liq) H2O(g)
which requires n = (10MJ)/(44.016kJ/mol) = 227.2 moles
and m = (227.2mol)(18g/mol) = 4.09kg