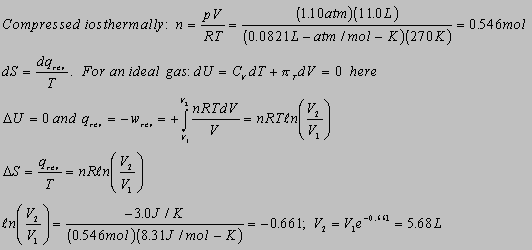
CHM 4410-01
September 28, 1998
Homework #5
Solutions
Chapter 4, Exercises #4.10(b), 4.11(b), 4.13(b), 4.14(b), 4.15(b),
4.17(b), 4.18(b), 4.22(b), 4.23(b); Problems # 4.1, 4.6, 4.12
4.10(b)
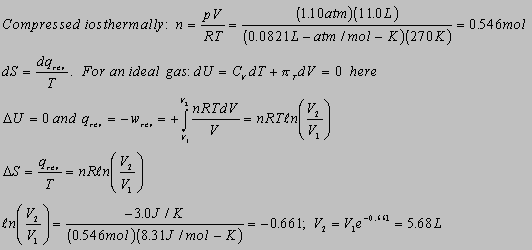
4.11(b)
Need a reversible path. In this case there are three steps: 1) cool
the 25g liquid from 50C to Tf; 2) warm the 70g sample from 10C
to Tf; 3) then mix the two samples at the same temperature together.
There is no entropy change for the system in step 3.
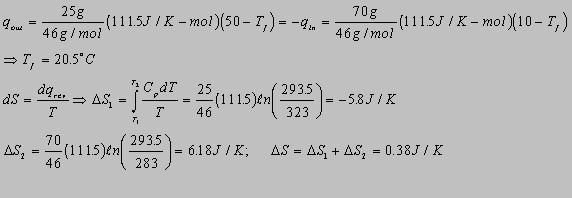
4.13(b)
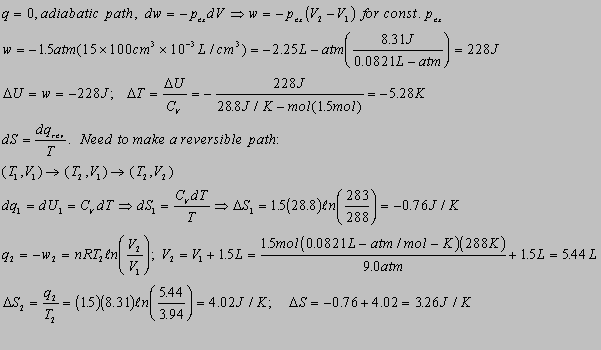
4.14(b)
CH3OH()CH3OH(g)
H = 35.27kJ/mol at 64.1C = 337K
Ssys = 35.27x103J/337K = 105J/K-mol
Ssurr. = -105J/K-mol for the reversible evaporation
4.15(b)
a) Zn(s) + Cu2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) + Cu(s)
Sr = -112.1 + 31.15 - 41.63 + 99.6 = -22.98J/K
b) C12H22O11(s) + 12O2(g) 12CO2 (g) + 11H2 O()
Sr = 11(69.91) + 12(213.74) - 12(205.138) - 360.2 = 512 J/K
4.17(b)
a) Gr = 0 - 147.6 - 0 -65.47 = -213 kJ
b) Gr = 12(-394.36) +11(-237.13) - 0 - (-1543) = -5798 kJ
4.18(b)
CO(g) + CH3OH() CH3COOH()
Hr = -484.5 - (-238.66) - (-110.53) = 135.3 kJ
Sr = 159.8 - 126.8 - 197.67 = -164.7 J/K
Gr = Hr - T Sr = = -135.3x103
J - 298K(-164.7 J/K) = -86.2 kJ
4.22(b)
C3H8(g) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 4H2O()
Gr = 3(-394.36) + 4(-237.13) - (-23.49) = -2108 kJ
The maximum non-p-V work the system can do to the surroundings is -Gr.
4.23(b)
a) the efficiency = (TH - TC)/TH = (1000-500)/1000 = 0.50
b) the efficiency = -w/qH = 0.5; -w = 0.50x1.0 kJ = 500 J
c) From energy conservation qH = w + qC . qC
= 500 J
4.6 (See 4.1 below.)
a) Reversible isothermal
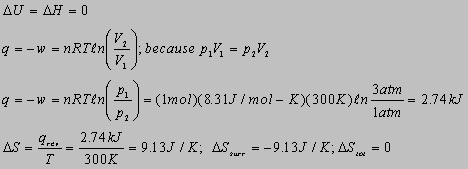
b) Constant pex

4.1
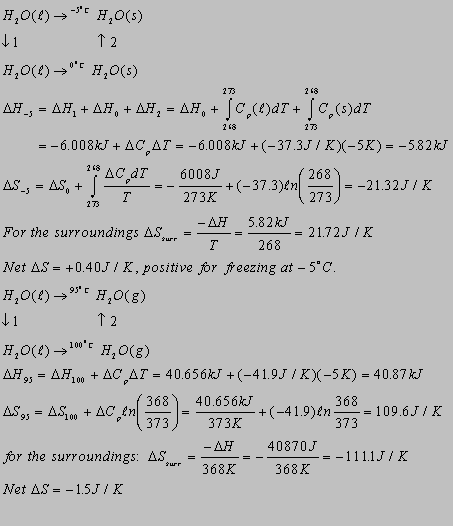
4.12
a) 200 g water at 0C added to 200 g water at 90C: obviously Tf = 45C
S = S1 + S2 = [(200g/18g/mol)(75.291J/K-mol)]{n(318/363)+n(318/273)}
= 5.48 J/K
b) 200 g ice at 0C added to 200 g water at 90C: need to melt the ice first.
If 200 g water is cooled from 90C to 0C, q = (200/18)(75.291)(-90)=-75.291kJ, which is enough heat to melt 75291J/{(6008J/mol)=12.53mol = 12.53x18g/mol=226g of ice.
All 200 g ice melts. This requires q1=(200g/18g/mol)(6008J/mol)=66.76kJ. This cools the hot water by (200g/18g/mol)(75.291J/K-mol)T=-66.76kJT=-79.8K or T2= 90- 79.8=10.2C. Now one has 200 g of water at 0C and 200 g at 10.2C. Mixing them together gives Tf = 5.1C. S = S1+S2+S3=[(6008)(200)/(18)(273)] + [(200/18)(75.291)n(278.1/273)] + [(200/18)(75.291)n(278.1/363)]=36.8 J/K