
|
Experiment 20 Alcohol Poisoning
|
Introduction/Background
Alcohol is a clear, relatively odorless chemical made up of three common molecules: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Drinking alcohol is called ethanol and has the formula CH3CHOH. Alcohol is also a psychoactive drug that changes brain chemistry and is lethal in high doses. Although we all know that alcohol causes intoxication, that drinking and driving is illegal and that the long term medical consequences of alcohol abuse can cause liver damage, what you may not be aware of is that deaths from alcohol overdoses occur about as often as those for other drugs.
Alcohol can cause death in two manners: One by debilitating those brain areas that control consciousness, respiration and heart rate. Or two, since alcohol is a central nervous system depressant, it can literally "turn off" these vital brain areas, resulting first in coma and then death.
For most people who drink too much alcohol what follows is a few hours of misery, "praying to the porcelian god". Vomiting is the body's attempt to eliminate any unabsorbed alcohol. The people who only vomit when they have consumed too much alcohol are in some strange manner the lucky ones. Some people just fall asleep (with or without vomiting) after they have consumed too much alcohol. It is these people for whom death can follow in one of two ways: One, they may fall into a deep sleep and vomit while sleeping and choke to death. Or two, they fall asleep and never wake up. This can occur when the concentration of alcohol is so high that the areas of the brain controlling life functions are so depressed that they stop altogether. |
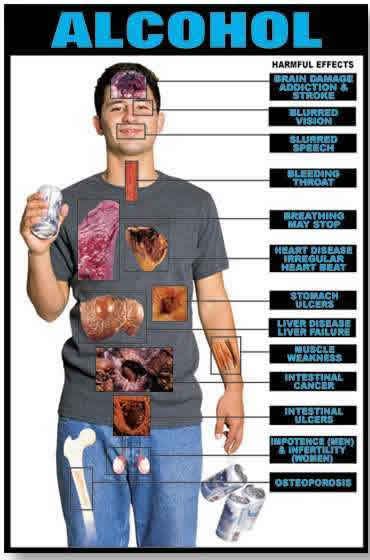
www.thelivercentre.com.au/.../ default.htm |
Key Concepts
How much alcohol is too much alcohol? There is a term called the "lethal dose" (LD). The "lethal dose" (LD) of alcohol is clinically defined "as the amount that would kill half the population (the LD50)". The LD50 is generally though to be about .40%. This is 5 times the current legal limit in the state of Florida. However, there are many cases in which death occurred from alcohol poisoning at much lower, and in some cases, much higher levels. For a 130 lb. man or woman drinking very quickly, it would only require about 10-14 drinks in an hour to reach the lethal level.
| Men |
| |
Approximate Blood Alcohol Percentage |
| Drinks |
Body Weight in Pounds |
|
| |
100 |
120 |
140 |
160 |
180 |
200 |
220 |
240 |
|
| 0 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
Only Safe
Driving Limit |
| 1 |
.04 |
.03 |
.03 |
.02 |
.02 |
.02 |
.02 |
.02 |
Impairment
Begins |
| 2 |
.08 |
.06 |
.05 |
.05 |
.04 |
.04 |
.03 |
.03 |
Driving
Skills
Significantly
Affected
Possible
Criminal
Penalties |
| 3 |
.11 |
.09 |
.08 |
.07 |
.06 |
.06 |
.05 |
.05 |
| 4 |
.15 |
.12 |
.11 |
.09 |
.08 |
.08 |
.07 |
.06 |
| 5 |
.19 |
.16 |
.13 |
.12 |
.11 |
.09 |
.09 |
.08 |
| 6 |
.23 |
.19 |
.16 |
.14 |
.13 |
.11 |
.10 |
.09 |
| 7 |
.26 |
.22 |
.19 |
.16 |
.15 |
.13 |
.12 |
.11 |
Legally
Intoxicated
Criminal
Penalties |
| 8 |
.30 |
.25 |
.21 |
.19 |
.17 |
.15 |
.14 |
.13 |
| 9 |
.34 |
.28 |
.24 |
.21 |
.19 |
.17 |
.15 |
.14 |
| 10 |
.38 |
.31 |
.27 |
.23 |
.21 |
.19 |
.17 |
.16 |
Subtract .01% for each 40 minutes of drinking.
One drink is 1.25 oz. of 80 proof liquor, 12 oz. of beer, or 5 oz. of table wine. |
|
| Women |
| |
Approximate Blood Alcohol Percentage |
| Drinks |
Body Weight in Pounds |
|
| |
90 |
100 |
120 |
140 |
160 |
180 |
200 |
220 |
240 |
|
| 0 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
.00 |
Only Safe
Driving Limit |
| 1 |
.05 |
.05 |
.04 |
.03 |
.03 |
.03 |
.02 |
.02 |
.02 |
Impairment
Begins |
| 2 |
.10 |
.09 |
.08 |
.07 |
.06 |
.05 |
.05 |
.04 |
.04 |
Driving Skills
Significantly
Affected
Possible
Criminal
Penalties |
| 3 |
.15 |
.14 |
.11 |
.10 |
.09 |
.08 |
.07 |
.06 |
.06 |
| 4 |
.20 |
.18 |
.15 |
.13 |
.11 |
.10 |
.09 |
.08 |
.08 |
| 5 |
.25 |
.23 |
.19 |
.16 |
.14 |
.13 |
.11 |
.10 |
.09 |
| 6 |
.30 |
.27 |
.23 |
.19 |
.17 |
.15 |
.14 |
.12 |
.11 |
Legally
Intoxicated
Criminal
Penalties |
| 7 |
.35 |
.32 |
.27 |
.23 |
.20 |
.18 |
.16 |
.14 |
.13 |
| 8 |
.40 |
.36 |
.30 |
.26 |
.23 |
.20 |
.18 |
.17 |
.15 |
| 9 |
.45 |
.41 |
.34 |
.29 |
.26 |
.23 |
.20 |
.19 |
.17 |
| 10 |
.51 |
.45 |
.38 |
.32 |
.28 |
.25 |
.23 |
.21 |
.19 |
Subtract .01% for each 40 minutes of drinking.
One drink is 1.25 oz. of 80 proof liquor, 12 oz. of beer, or 5 oz. of table wine. |
|
Data supplied by the Pennsylvania Liquor Control Board. |
How can you tell is someone has been poisoned? The symptoms of an alcohol overdose are vomiting, loss of consciousness, deep sleep (cannot be awakened) and slow, shallow breathing.
|
Blood Alcohol Limits
|
|
State
|
BAC Limit%
|
|
Alabama
|
0.08
|
|
Alaska
|
0.10
|
|
Arizona
|
0.10
|
|
Arkansas
|
0.10
|
|
California
|
0.08
|
|
Colorado
|
0.10
|
|
Connecticut
|
0.10
|
|
Delaware
|
0.10
|
|
District of Columbia
|
0.08
|
|
Florida
|
0.08
|
|
Georgia
|
0.08
|
|
Hawaii
|
0.08
|
|
Idaho
|
0.08
|
|
Illinois
|
0.08
|
|
Indiana
|
0.10
|
|
Iowa
|
0.10
|
|
Kansas
|
0.08
|
|
Kentucky
|
0.08
|
|
Louisiana
|
0.10
|
|
Maine
|
0.08
|
|
Maryland
|
0.10
|
|
Massachusetts
|
no per se law
|
|
Michigan
|
0.10
|
|
Minnesota
|
0.10
|
|
Mississippi
|
0.10
|
|
Missouri
|
0.10
|
|
Montana
|
0.10
|
|
Nebraska
|
0.10
|
|
Nevada
|
0.10
|
|
New Hampshire
|
0.08
|
|
New Jersey
|
0.10
|
|
New Mexico
|
0.08
|
|
New York
|
0.10
|
|
North Carolina
|
0.08
|
|
North Dakota
|
0.10
|
|
Ohio
|
0.10
|
|
Oklahoma
|
0.10
|
|
Oregon
|
0.08
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
0.10
|
|
Rhode Island
|
0.10
|
|
South Carolina
|
0.10
|
|
South Dakota
|
0.10
|
|
Tennessee
|
0.10
|
|
Texas
|
0.08
|
|
Utah
|
0.08
|
|
Vermont
|
0.08
|
|
Virginia
|
0.08
|
|
Washington
|
0.08
|
|
West Virginia
|
0.10
|
|
Wisconsin
|
0.10
|
|
Wyoming
|
0.10
|
Data taken from http://www.q3alcoholdetectors.com/statebaclimits.html.
|
Glossary
Psychoactive = A psychoactive drug or psychotropic substance is a chemical that alters brain function, resulting in temporary changes in perception, mood, consciousness, or behavior. Such drugs are often used in recreational drug use and as entheogens for spiritual purposes, as well as in medication, especially for treating neurological and psychiatric illnesses.
Related Materials
B.R.A.D. Alcohol Poisoning (http://www.brad21.org/alcohol_poisoning.html)
Binge Drinking (http://www.collegedrinkingprevention.gov/ students/risky/alcoholpoisoning.aspx)
A.D.A.P.T. Alcohol Poisoning (http://healthcenter.ucdavis.edu/alcoholpoisoning.html)

